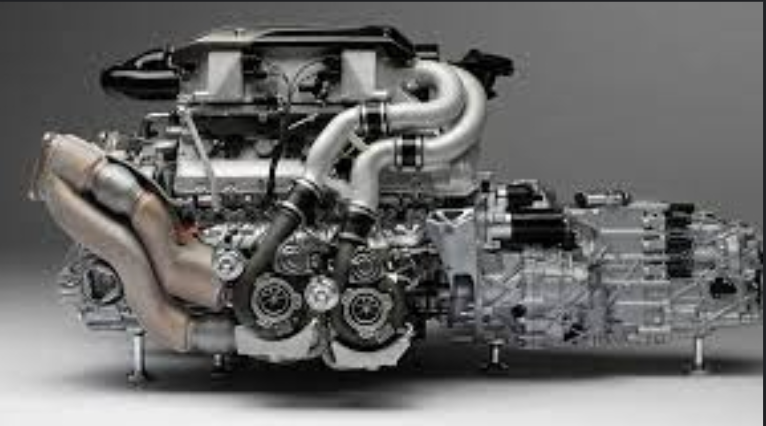
A turbocharger, often referred to simply as a "turbo," is a device used in internal combustion engines to increase the efficiency and power output of the engine.
 |
| Turbocharged Engines |
Turbocharged Engines
A turbocharger, often referred to simply as a "turbo," is a device used in internal combustion engines to increase the efficiency and power output of the engine. It operates by forcing more air into the engine's combustion chamber, which allows for a greater amount of fuel to be burned, resulting in increased power generation.
Here's how a turbocharger works:
- Exhaust Gas Energy Conversion: The turbocharger is typically mounted on the exhaust manifold of the engine. As the engine burns fuel in the combustion chamber, it generates exhaust gases that contain a substantial amount of energy in the form of heat and pressure.
- Turbine Wheel: The exhaust gases are directed towards the turbine wheel within the turbocharger. The force of the exhaust gases causes the turbine wheel to spin rapidly. This spinning motion converts the energy from the exhaust gases into kinetic energy.
- Compressor Wheel: The turbine wheel and the compressor wheel are connected on a common shaft. As the turbine wheel spins, it drives the compressor wheel to also spin.
- Compressed Air Intake: The compressor wheel draws in and compresses air from the surroundings, effectively increasing the air pressure before it enters the engine's intake manifold.
- Increased Air-Fuel Mixture: The compressed air from the compressor wheel is forced into the engine's cylinders at a higher pressure than atmospheric pressure. This allows the engine to burn more fuel in each combustion cycle, resulting in more power being produced.
- Increased Power Output: With more air available for combustion, the engine can burn a larger amount of fuel, leading to increased power output. This process is commonly referred to as "forced induction."
Read Also : Types of Piston
Turbochargers are commonly used in both gasoline and diesel engines to boost their power without significantly increasing the engine's size. They are particularly effective at higher engine speeds, where exhaust gas flow is stronger and can spin the turbine wheel faster, thereby providing greater levels of boost pressure.
Read also:Types of Fuel Pumps
However, there are also some challenges associated with turbochargers, such as "turbo lag," which is the delay between pressing the accelerator and experiencing the increased power due to the time it takes for the exhaust gases to build up enough momentum to spin the turbine wheel effectively.
Read ajso: Major Systems and Components of an Automobile
In recent years, turbocharger technology has advanced significantly, with improvements in materials, aerodynamics, and electronic control systems, helping to minimize issues like turbo lag and making turbocharged engines more responsive and efficient.
Read also Car Engine Parts



0 Comments