Steam Boiler Technology:The world energy consumption has doubled in the last thirty years and it keeps on increasing with about 1.5% per year .While the earth's oil and gas reserves are expected to deplete after less than a hundred years.
 |
| Steam Boiler Technology |
Steam Boiler Technology
The contents of the book
- The Basics Of Steam Generation
- The History Of Steam Generation
- Modern Boiler Types and Applications
- Steam / Water Circulation Design
- Feedwater and Steam System Components
- Combustion Process Equipment
- Heat Exchangers in Steam Boiler
- Boiler Calculations
- Thermal Design of Heat Exchangers
- Circulating Fluidized Bed Boiler Design
- Recovery Boilers
Introduction
The world energy consumption has doubled in the last thirty years and it keeps on increasing with about 1.5% per year (Figure 1). While the earth's oil and gas reserves are expected to deplete after less than a hundred years, the coal reserves will last for almost five hundred years into the future (taking into account estimations of fossil fuel reserves that have not yet been found) (Figure 2). In Finland, 50% of the electrical power produced, is produced in steam power plants. But there are more reasons to why electricity generation based on steam power plant will continue to grow and why there still will be a demand for steam boilers in the future:
- The world-wide dependency upon fossil fuels for power production (Figure 1, Figure 2, and Figure 3)
- The cost of the produced electricity is low.
- The technology has been used for many decades and is reliable and available.
- Wind and solar power are still expensive compared to steam power.
- The environmental impact of coal powered steam plants have under the past decade been heavily diminished thanks to improved SOx and NOx reduction technology.
- The paper industry uses steam boilers as a vital utility to recycle chemicals and derive electricity from black liquor (pulping waste).
- Waste and biofuels can effectively be combusted in a boiler [1].
 |
| world consumption of primary energy |
Basics of boilers and boiler processes
In a traditional context, a boiler is an enclosed container that provides a means for heat from combustion to be transferred into the working media (usually water) until it becomes heated or a gas (steam). One could simply say that a boiler is as a heat exchanger between fire and water. The boiler is the part of a steam power plant process that produces the steam and thus provides the heat.The steam or hot water under pressure can then be used for transferring the heat to a process that consumes the heat in the steam and turns it into work. A steam boiler fulfils the following statements:
- It is part of a type of heat engine or process
- Heat is generated through combustion (burning)
- It has a working fluid, a.k.a. heat carrier that transfers the generated heat away from the boiler
- The heating media and working fluid are separated by walls.
In an industrial/technical context, the concept “steam boiler” (also referred to as “steam generator”) includes the whole complex system for producing steam for use e. g. in a turbine or in industrial process. It includes all the different phases of heat transfer from flames to water/steam mixture (economizer, boiler, superheater, reheater and air preheater). It also includes different auxiliary systems (e. g. fuel feeding, water treatment, flue gas channels including stack). [3]
The heat is generated in the furnace part of the boiler, where fuel is combusted. The fuel used in a boiler contains either chemically bonded energy (like coal, waste and biofuels) or nuclear energy. Nuclear energy will not be covered in this material. A boiler must be designed to absorb the maximum amount of heat released in the process of combustion. This heat is transferred to the boiler water through radiation, conduction and convection. The relative percentage of each is dependent upon the type of boiler, the designed heat transfer surface and the fuels that power the combustion.
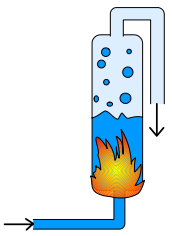
A simple boiler
In order to describe the principles of a steam boiler, consider a very simple case, where the boiler simply is a container,partially filled with water (Figure 4).
Combustion of fuel produce heat, which is transferred to the container and makes the water evaporate. The vapor or steam can escape through a pipe that is connected to the container and be transported elsewhere. Another pipe brings water (called “feedwater”) to the container to replace the water that has evaporated and escaped.
DOWNLAD also Foam Fire Extinguishing System Calculations Excel Sheet .




0 Comments